Request Audit
Overview
The QueryPie proxy monitors and records audit logs for each call of API server call history to Kubernetes clusters managed by the organization.
Viewing Request Audit
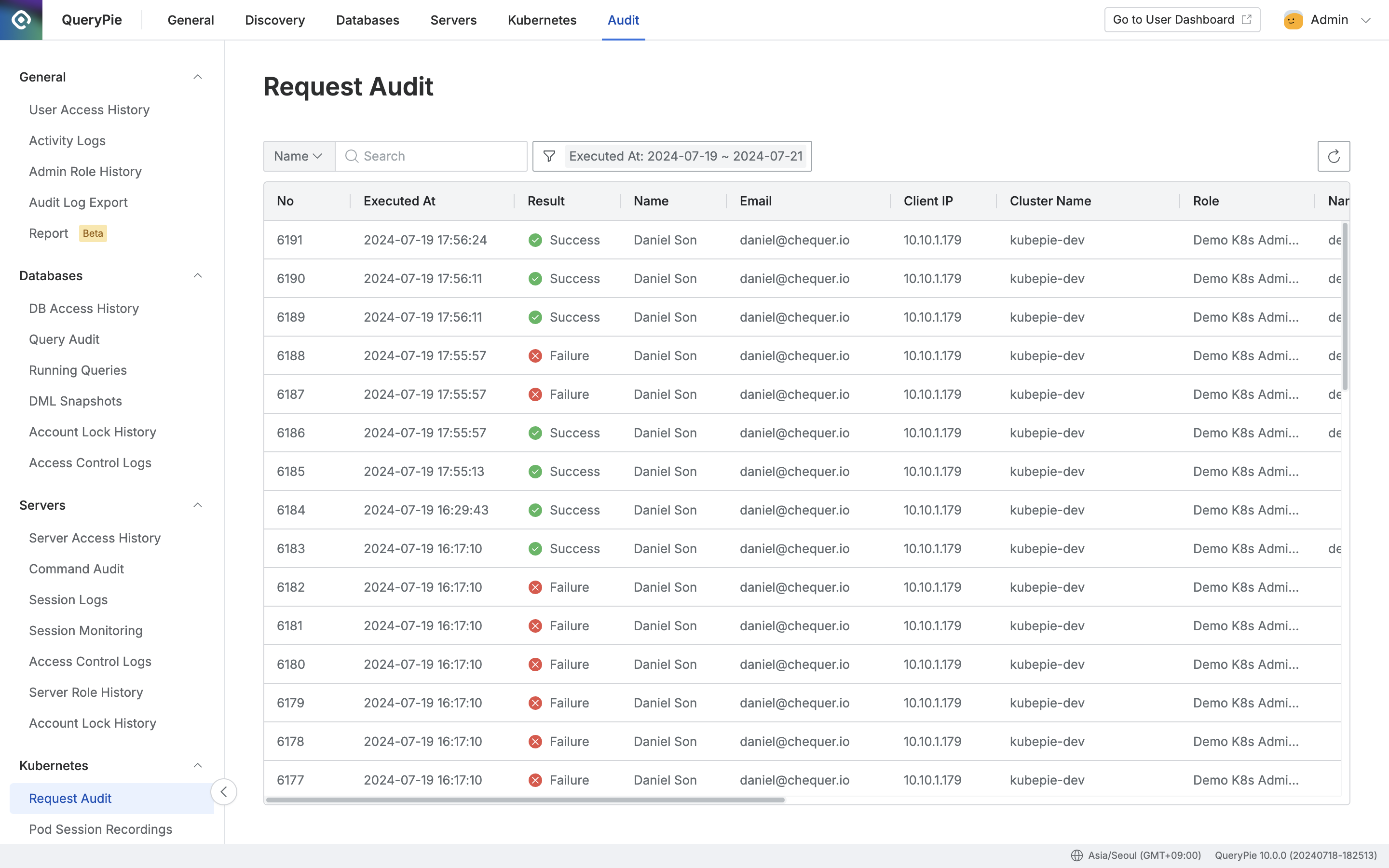
- Navigate to the Administrator > Audit > Kubernetes > Request Audit menu.
- Logs are displayed in descending order based on Executed At from 00:00 to 23:59 of the current day.
- You can search with the following conditions through the search field in the top left of the table:
- Name : User name
- Cluster Name : Cluster name registered in QueryPie
- Click the filter button on the right side of the search field to filter with AND/OR conditions for the following:
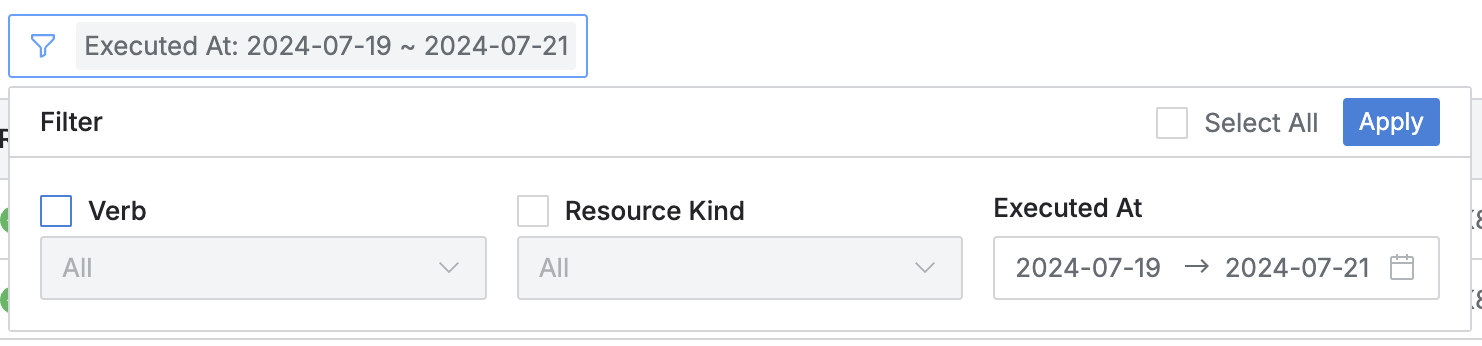
- Verb : Specific Kubernetes API action called
get,list,watch,create,update,patch,delete,deletecollection
- Resource : Specific Kubernetes resource called
pods,pods/exec,pods/log,pods/portforward,services,ingresses,deployments,replicasets,statefulsets,daemonsets,configmaps,secrets,namespaces,nodes,persistentvolumes,persistentvolumeclaims,jobs,cronjobs,serviceaccounts,endpoints,roles,rolebindings,clusterroles,clusterrolebindings,othersothersis used to filter items that do not correspond to other custom resources, etc.
- Executed At : Kubernetes API call occurrence date and time range
- You can refresh the log list through the refresh button in the top right of the table.
- The table provides the following column information:
- No : Event identification number
- Executed At : Kubernetes API call occurrence date and time
- Result : API call success/failure status
- ✔️ Success
- ❌ Failure
- Name : Target user name
- Email : Target user email
- Client IP : User client IP address
- Cluster Name : Target Kubernetes cluster name
- Role : Role name that could perform the action
- Namespace : Target namespace
- Verb : Specific Kubernetes API action called
- Resource : Specific Kubernetes resource called
- Resource Name : Name of the specific Kubernetes resource called
- Message : Records messages returned during API calls
- QueryPie records a total of 2 times for session logs such as pods/exec, matching the start and end times of each session. The distinction can be made through the corresponding message.
- Cluster Endpoint : Target API endpoint called
- Kubernetes Groups : Kubernetes group account name that QueryPie Proxy impersonated during API calls
- Client Name : User client name/version (e.g. kubectl/v1.27.3)
Viewing Request Audit Details
- You can view detailed information by clicking on each row.
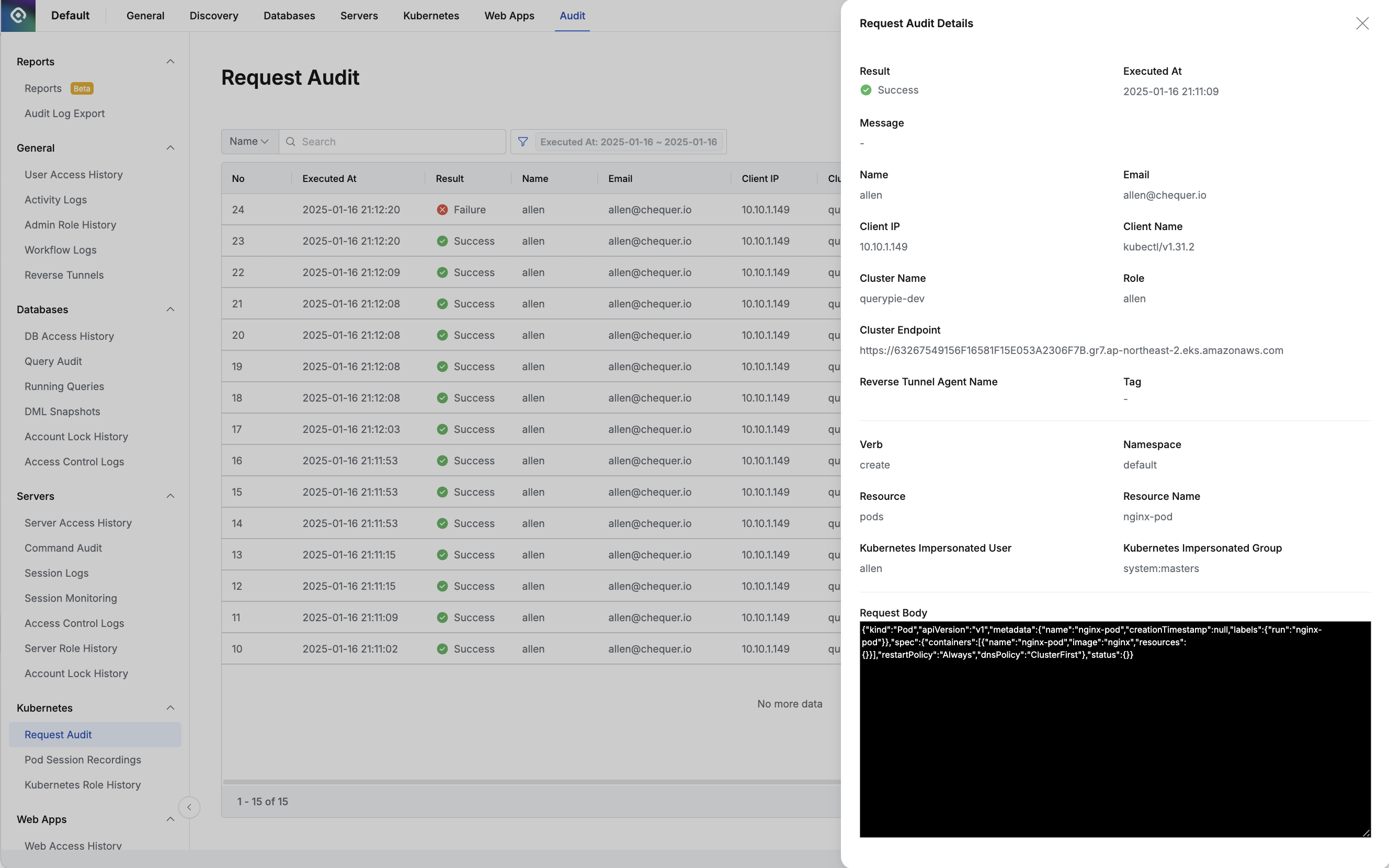
- The top displays information based on basic events:
- Result : API call success/failure status
- ✔️ Success
- ❌ Failure
- Executed At : Kubernetes API call occurrence date and time
- Message : Records messages returned during API calls
- Name : Target user name
- Email : Target user email
- Client IP : User client IP address
- Client Name : User client name/version
- Cluster Name : Target Kubernetes cluster name
- Role : Role name that could perform the action
- Cluster Endpoint : Target API endpoint called
- Reverse Tunnel Agent Name : When connected through Reverse Tunnel, the name of the Reverse Tunnel Agent used for communication
- Tag : When connected through Reverse Tunnel, the Tag used to select the Reverse Tunnel Agent for communication
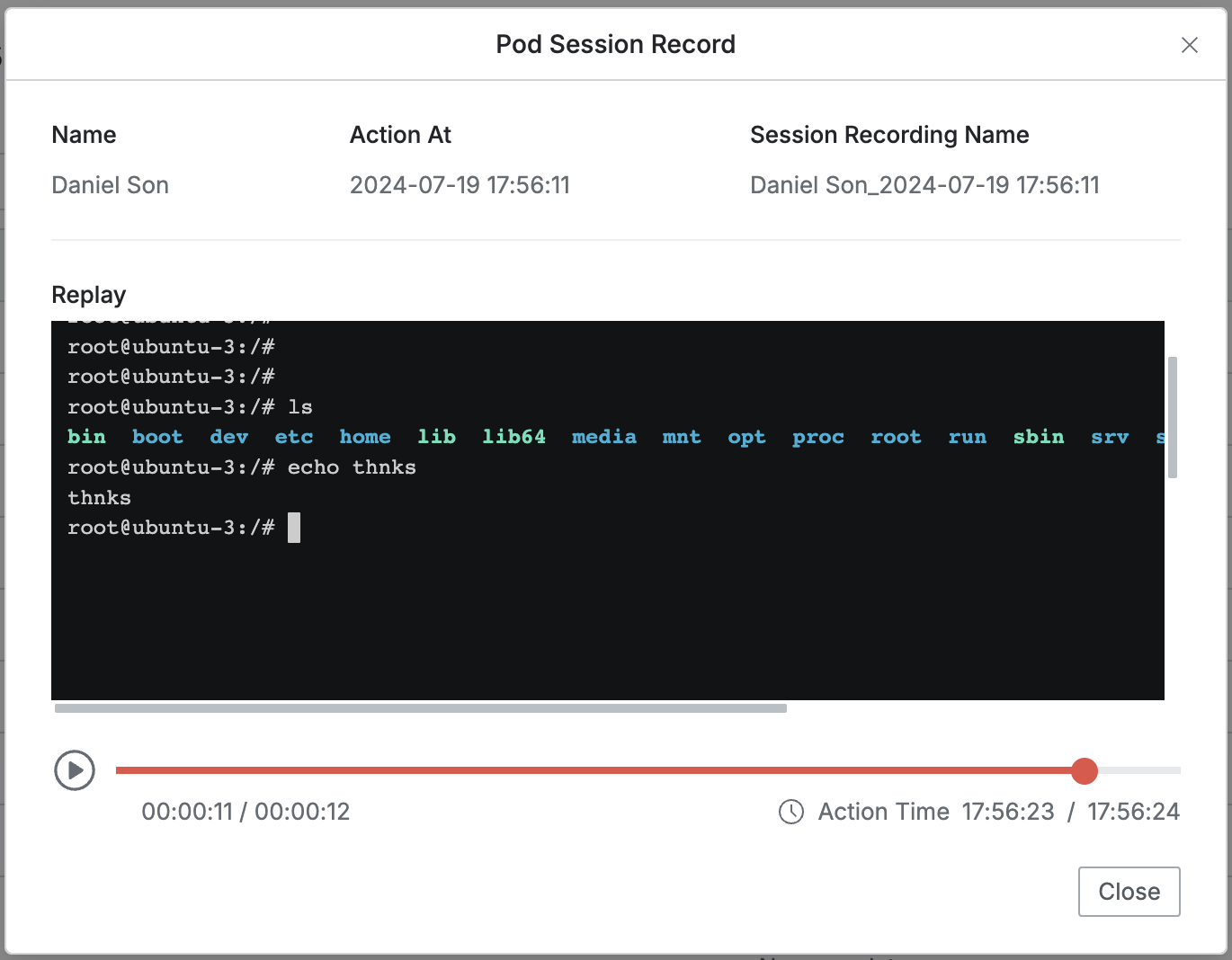
- Pod Session Recording : Recording for the corresponding session when executed with Pod exec API
- This field is viewable in the detail page only for logs where session recording occurred.
- When executed with Pod exec API, recording for the corresponding session proceeds, and the “Session Recording” text includes a hyperlink.

- Clicking the link plays the related session recording.
- The middle section displays information based on API call history:
- Verb : Specific Kubernetes API action called
- Namespace : Target namespace
- Resource : Specific Kubernetes resource called
- Resource Name : Name of the specific Kubernetes resource called
- Kubernetes Impersonated User : Kubernetes user account name impersonated during API calls (expresses —as information)
- Kubernetes Impersonated Group : Kubernetes group account name impersonated during API calls (expresses —as-group information)
- The Request Body area at the bottom specifies what YAML content was requested via API.
- Mainly records content in Create, Update, Patch history.
- The Max Size for Request Body is recorded and stored up to a maximum of 4KB.
- When a situation exceeding 4KB occurs, the corresponding kubernetes API call is processed as is, and the record remains only up to 4KB.
- Result : API call success/failure status
Last updated on