Data Policies
Overview
Data Policies is a feature for setting and managing data governance policies in QueryPie, such as data access control, data masking, and enforcement of usage reason input. Through this feature, you can manage data security, privacy protection, and regulatory compliance.
Accessing Policy Creation Screen
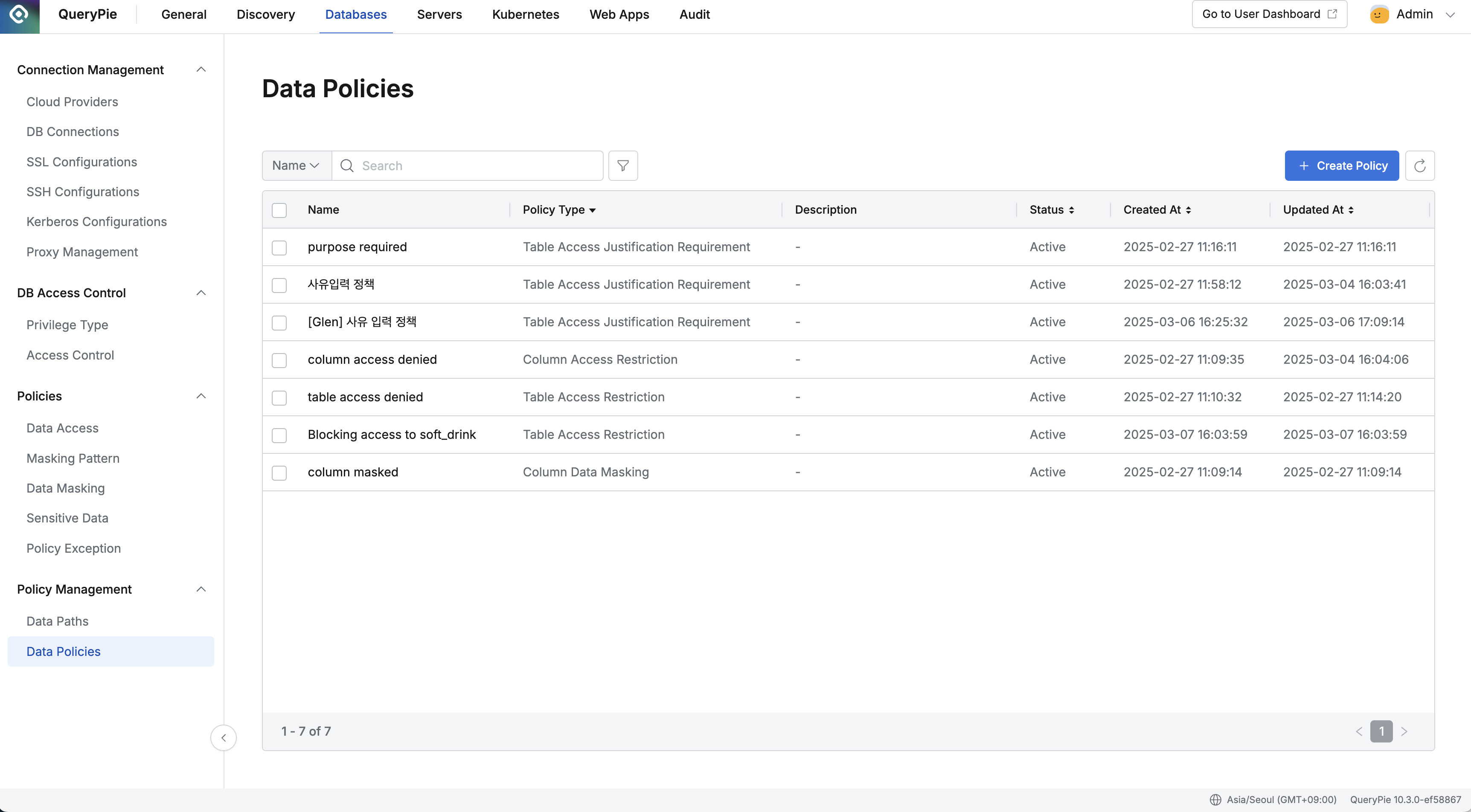
- Expand the Policy Management section in the left sidebar.
- Data Policies Click the menu.
- Click the Create Policy button at the top to navigate to the policy creation screen.
Setting Basic Policy Information
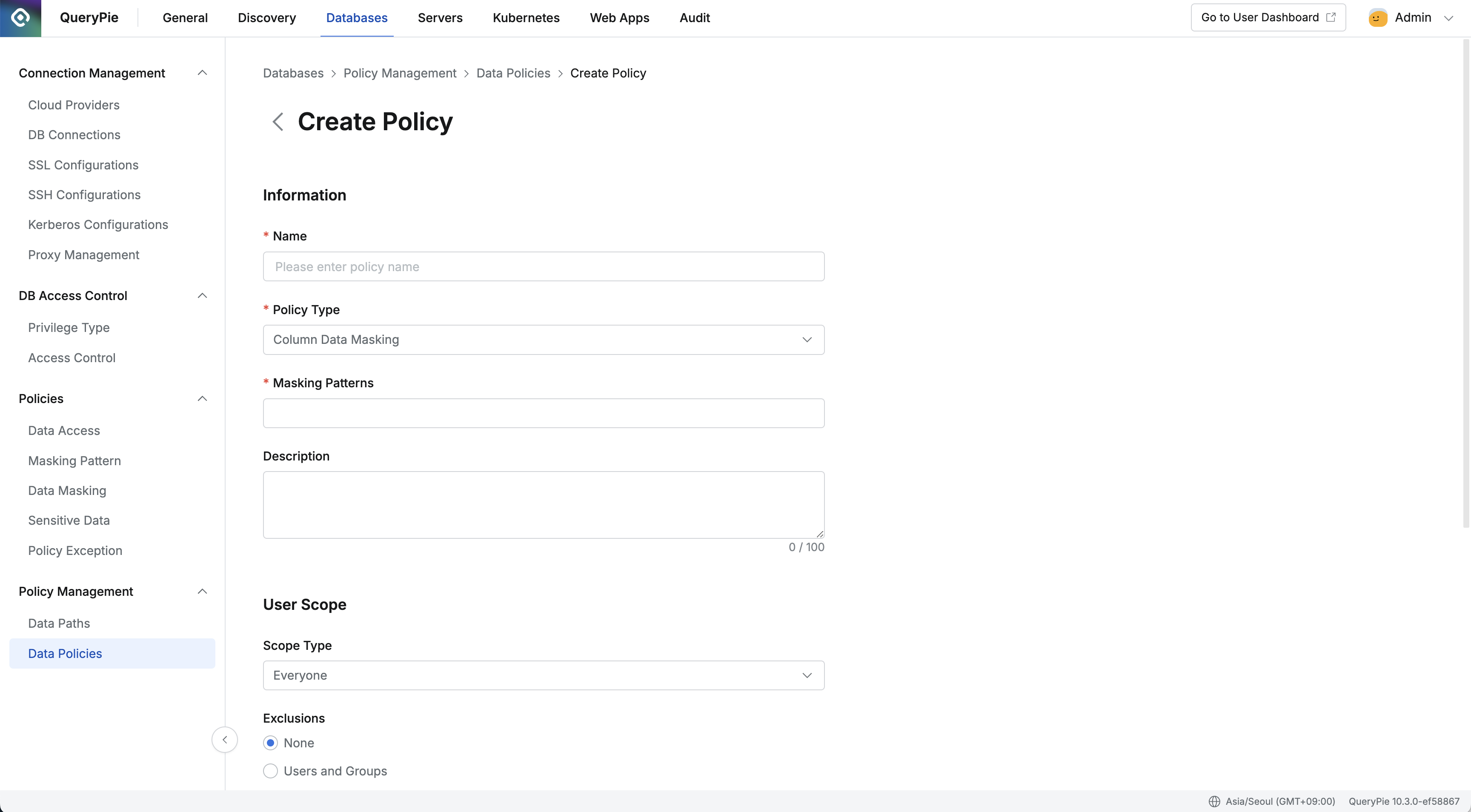
In the Information section of the policy creation screen, set the following information:
- Name: Enter the name of the policy. (Required)
- Policy Type : Select the policy type to apply from the dropdown menu. (Required)
- Description: Enter a description of the policy. (Optional)
Policy Type Introduction
QueryPie provides the following policy types:
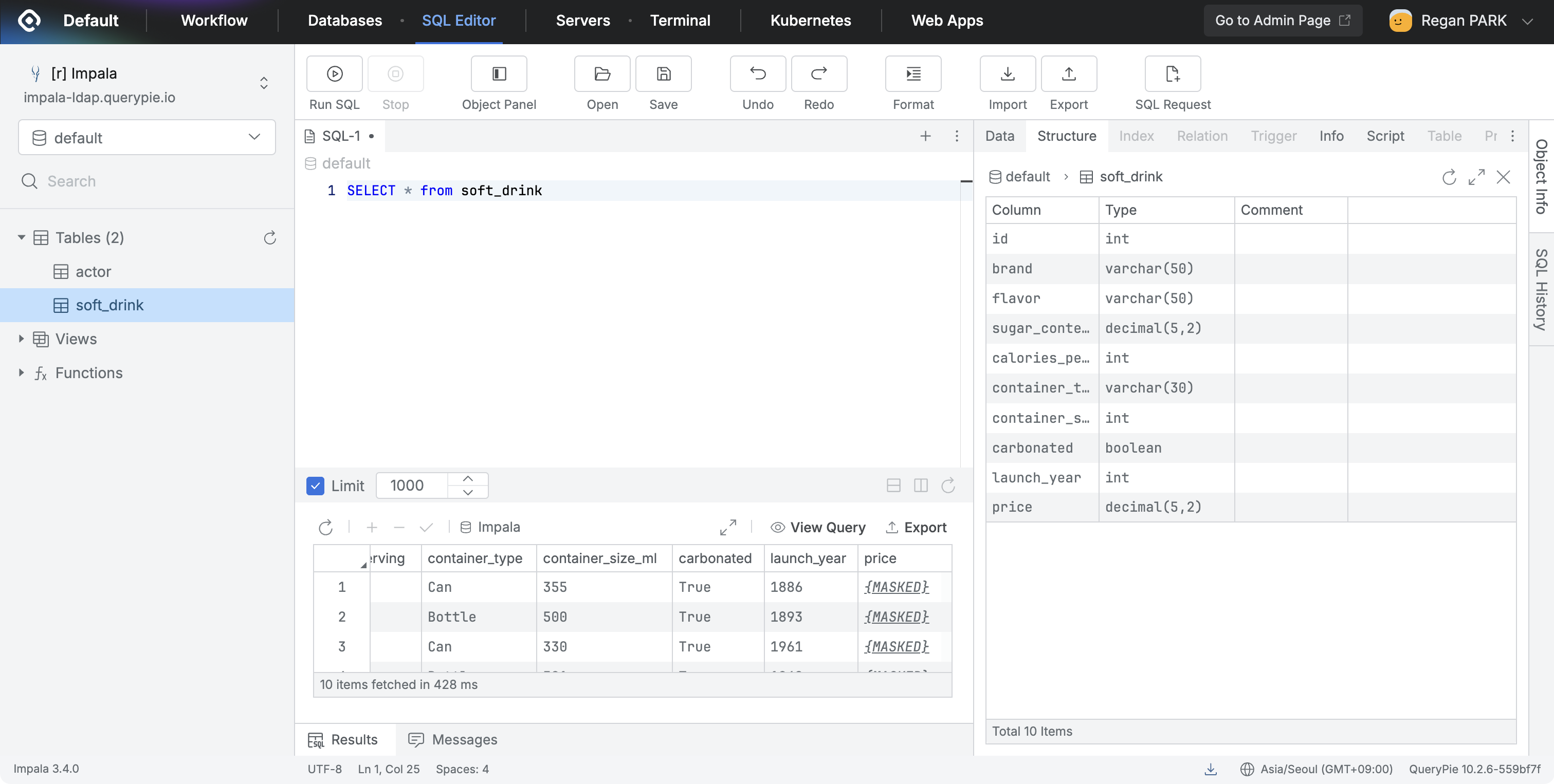
- Column Data Masking
- Applies data masking policy to columns.
- Uses regex-based masking patterns to detect and mask specific data patterns. (Masking Patterns)
- When users query the column, it displays as
{masked}and clicking the cell shows the masked data.
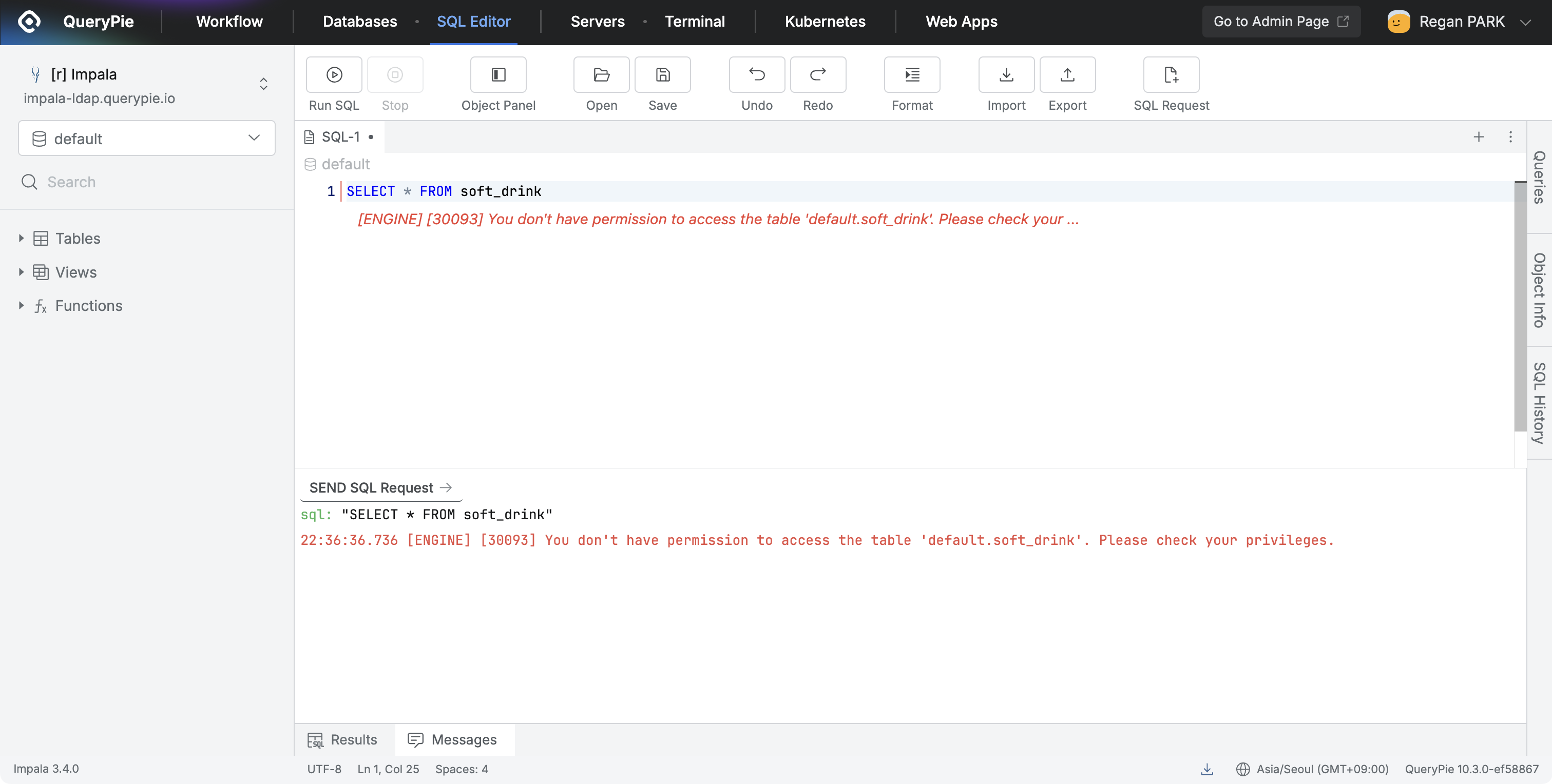
- Table Access Restriction
- Applies access blocking policy to tables.
- When users try to query the table, access is blocked and a no permission message is displayed.
- Message:
"You don't have permission to access the table 'database.table'. Please check your privileges."
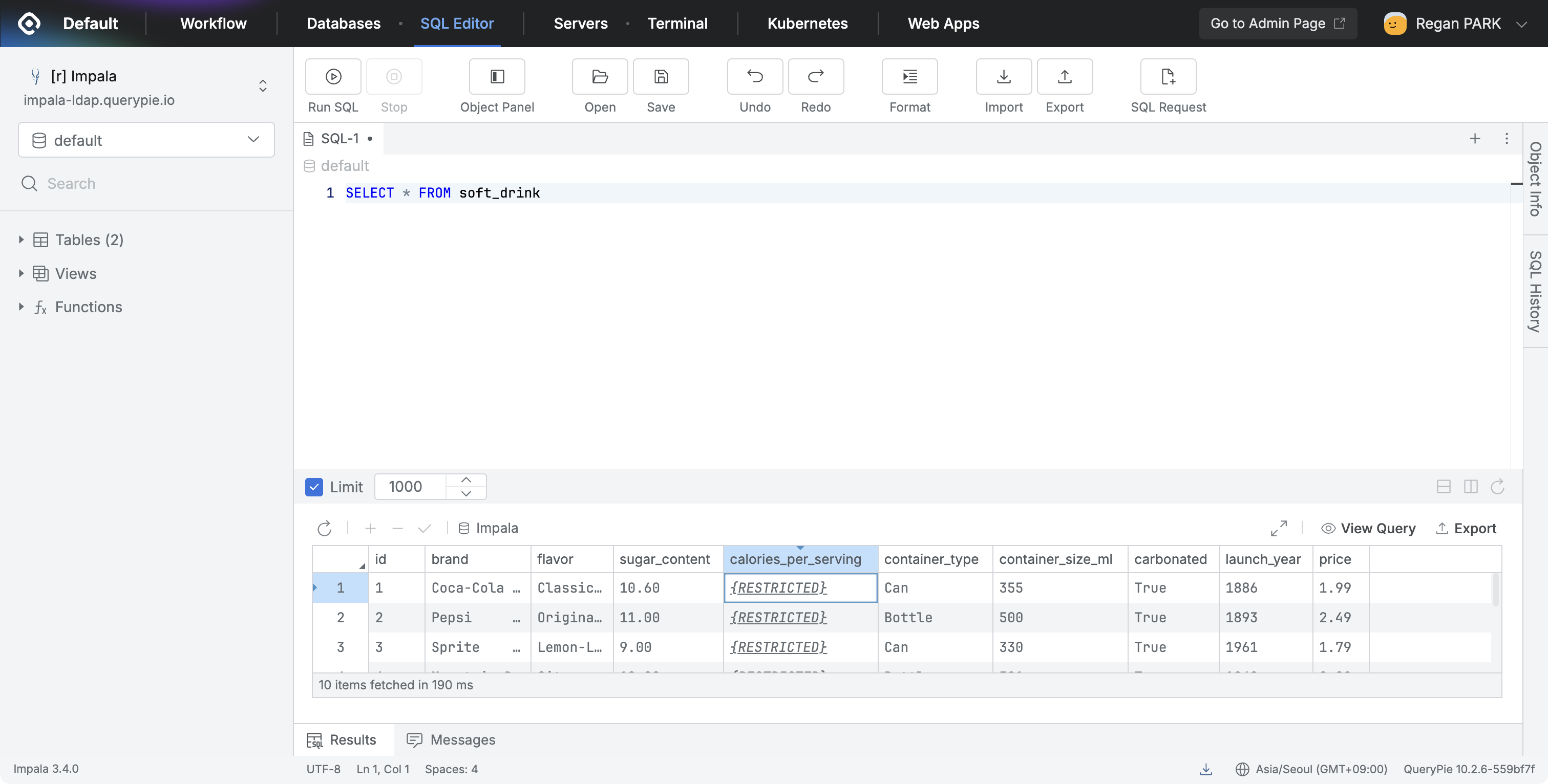
- Column Access Restriction
- Applies access blocking policy to columns.
- When users try to query the column, it displays as
{restricted}and access is blocked.
- Table Access Justification Requirement
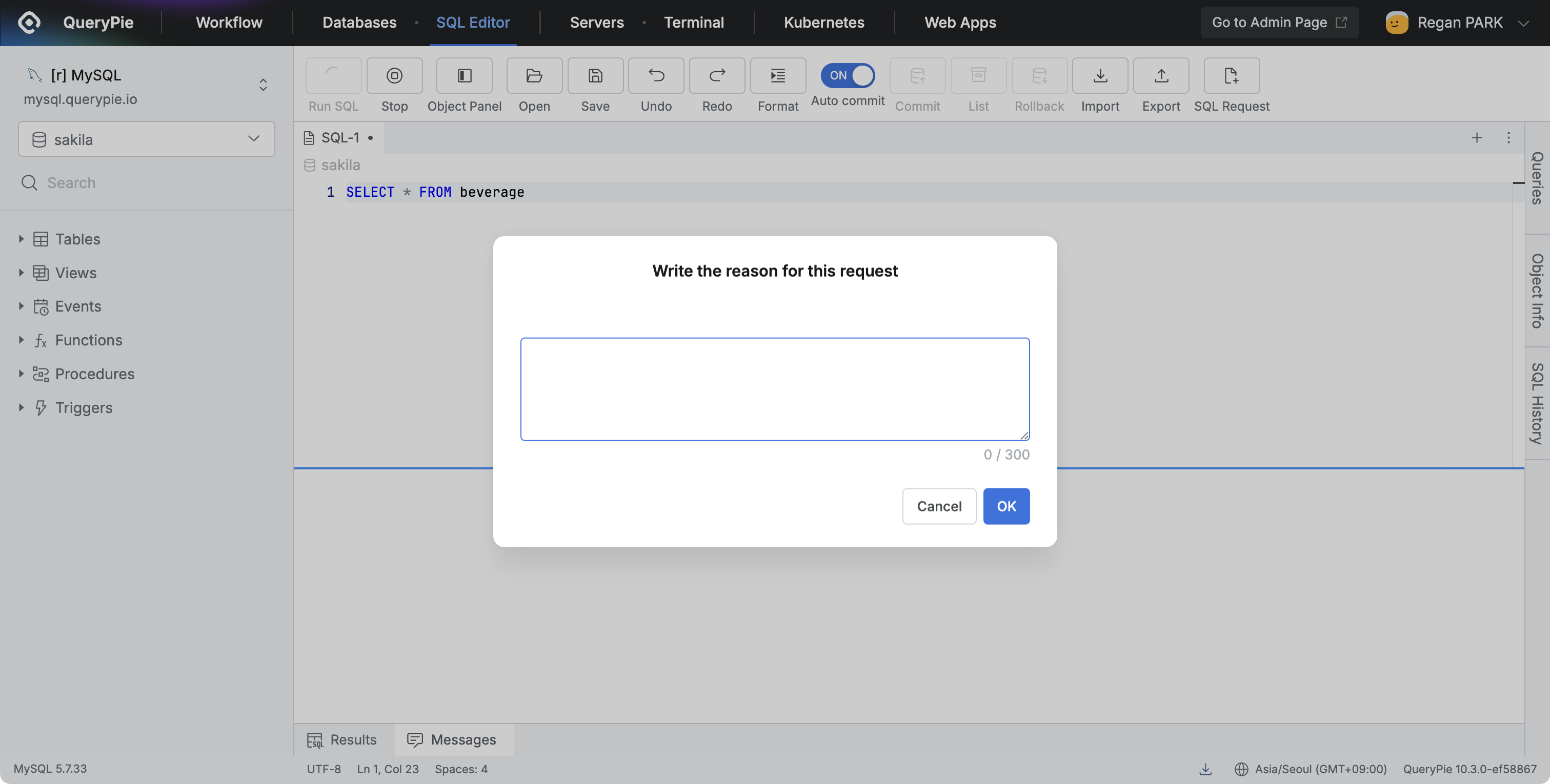
- Enforces reason input when performing operations on specific tables.
- When users perform selected operations (e.g., SELECT queries, data export), a reason input modal is displayed.
- The entered reason is recorded in the Execution Reason of Query Audit.
- Sensitive Data Access Monitoring
- Allows administrators to designate specific tables or columns as sensitive information and generate alerts when accessed.
- Set which paths are sensitive information, and configure alert settings in General > Company Management > Alert.
(As of 11.0.0, the Sensitive Data Access Monitoring Alert configuration feature for new policies is not yet implemented.)
- DML Query Approval Enforcement
- Forces approval procedures through Workflow when performing
INSERT,UPDATE,DELETEqueries on specific tables. - Before creating this policy, you must first create an Approval Rule of SQL Request Type in General > Workflow Management > Approval Rules. Performing
INSERT,UPDATE,DELETEassumes that the person performing has the corresponding privilege. To allow the person executing the query to be the requester, the “Allow Assignee selection (All Users)” option must be selected in the Execution item’s Assignee for Execution as shown in the figure below, so that people withINSERT,UPDATE,DELETEprivileges but who are not administrators can execute queries through approval.
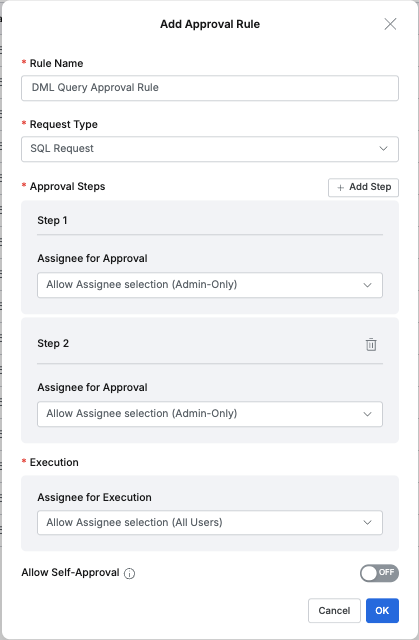
General > Workflow Management > Approval Rules creating SQL Request format Approval rule
- If an Approval Rule is created, you can specify the Approval Rule to link with the policy as shown in the figure below.
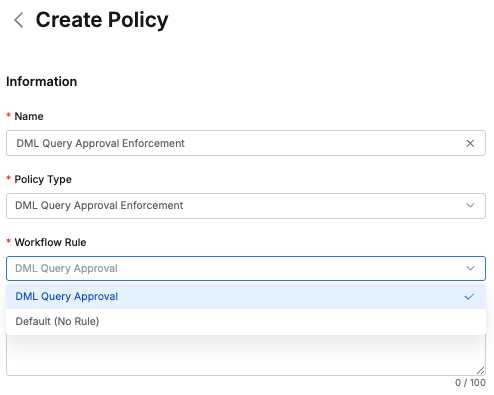
Databases>Policy Management>Data Policies specifying pre-created SQL Request format Approval Rule
- DML Query Approval Enforcement cannot specify targets by tags and must specify specific paths using specific data path.
- Forces approval procedures through Workflow when performing
Setting Policy Application Targets
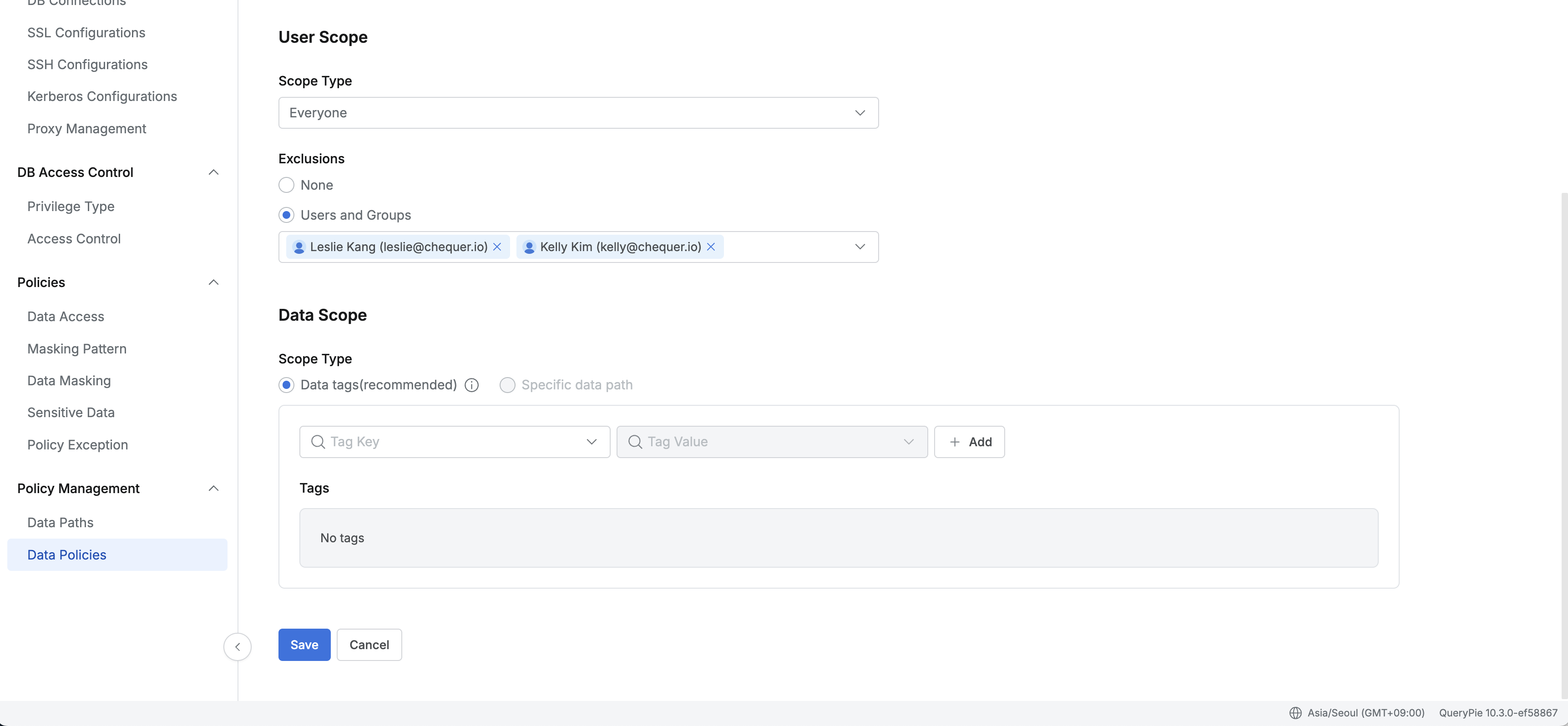
In the User Scope section of the policy creation screen, set the user scope to which the policy will be applied.
Scope Type
- Everyone: The policy applies to all users. (Default)
- Users or Groups: The policy applies only to selected specific users or groups.
- Attribute of Users : Used when you want to dynamically apply policies to users with specific attributes. 11.1.0
Exclusions
You can set targets to exclude from policy application. User scope’s scope type is Everyone Only when Exclusions can be specified. The difference from specifying through Policy Exception is that Policy Exception has a set period for the exception, but Exclusion targets have the same lifecycle as the policy. That is, they are always applied while the policy exists. (Policy application targets = All - specific users or groups specified in exclusions.)
- None: Applies to all users according to Scope Type without exclusions. (Default)
- Users and Groups: Excludes selected users or groups from policy application.
Setting Policy Target Data
In the Data Scope section of the policy creation screen, set the data to which the policy will be applied.
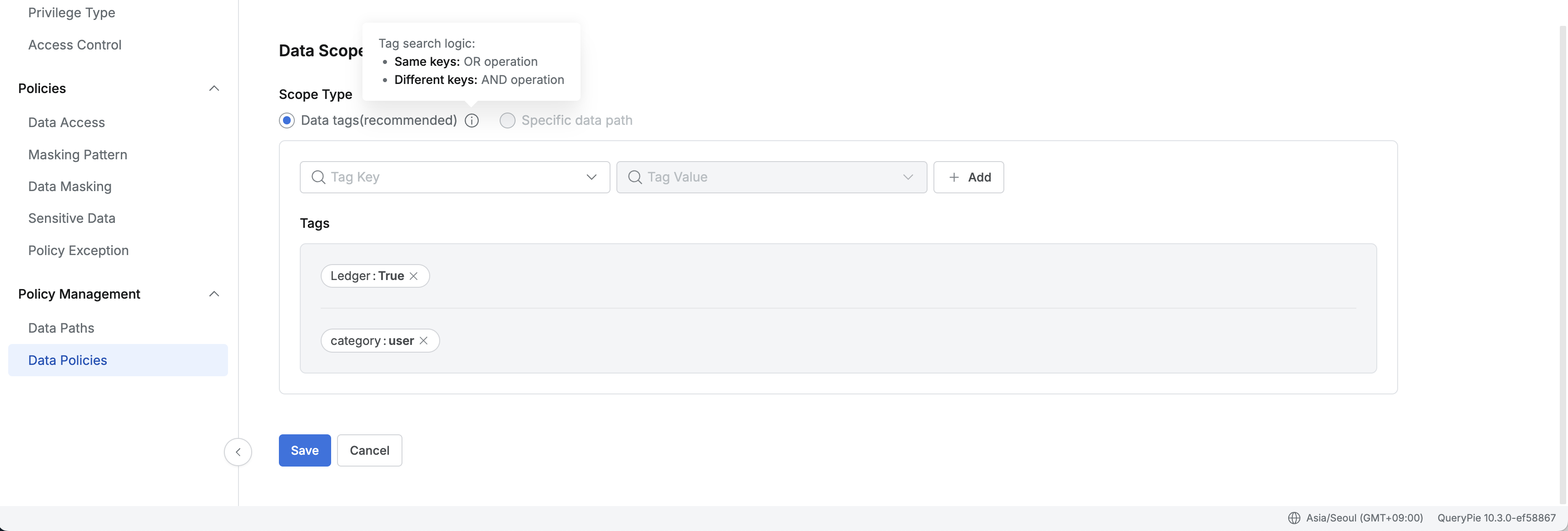
Scope Type
In 11.3.0, regular expressions can be used when selecting specific data path for all policy types. Also, multiple tables or columns can be selected and registered as targets.
- Data tags: Select policy application targets based on tags set in the Data Paths menu.
- When this option is selected, you can select tables or columns to apply the policy by specifying tag keys and values.
- Specific data path : An option to directly specify specific data paths. 11.0.0
- After selecting this option, click the Add target button to specify Database, Schema, Table, Column in the popup dialog, and regular expressions can also be used.
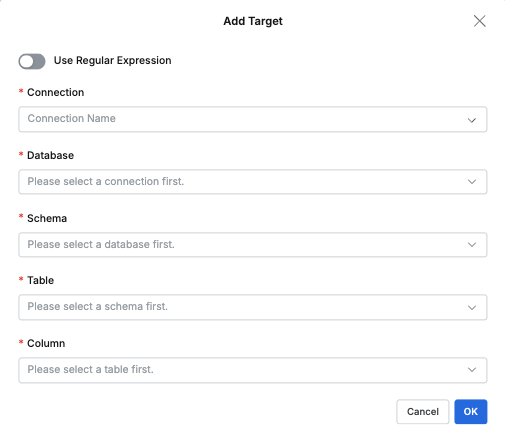
Direct path specification
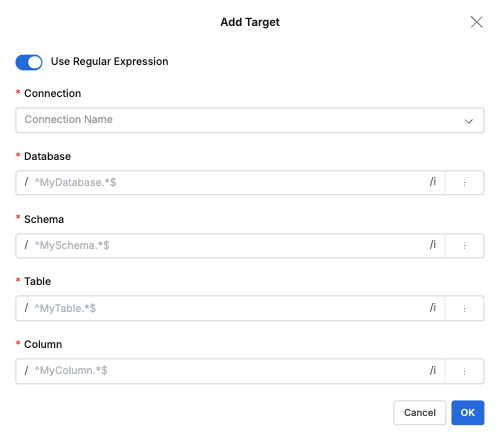
Specifying targets using regular expressions
- After selecting this option, click the Add target button to specify Database, Schema, Table, Column in the popup dialog, and regular expressions can also be used.
Saving Policy
When all settings are complete, click the Save button at the bottom of the screen to save the policy. To cancel saving, click the Cancel button.
Important Notes
- Since policy settings are based on data tags, appropriate tags must be assigned in the Data Paths menu before setting policies.
- Policies only support the database types listed below, and cannot be applied to unsupported database types.
- MySQL, MariaDB, Impala, Single Store, Hive, BigQuery, Oracle, PostgreSQL, SQLServer, Redshift, MS SQL Azure, SAP Hana, Trino, Athena, MongoDB, DocumentDB, Cassandra, ScyllaDB, DynamoDB, Redis