Manually Registering Kubernetes Clusters
Overview
QueryPie allows you to manually register Kubernetes clusters located on-premises or elsewhere to apply access control.
Manually Registering Clusters
To manually register individual servers, you need to enter basic server information.
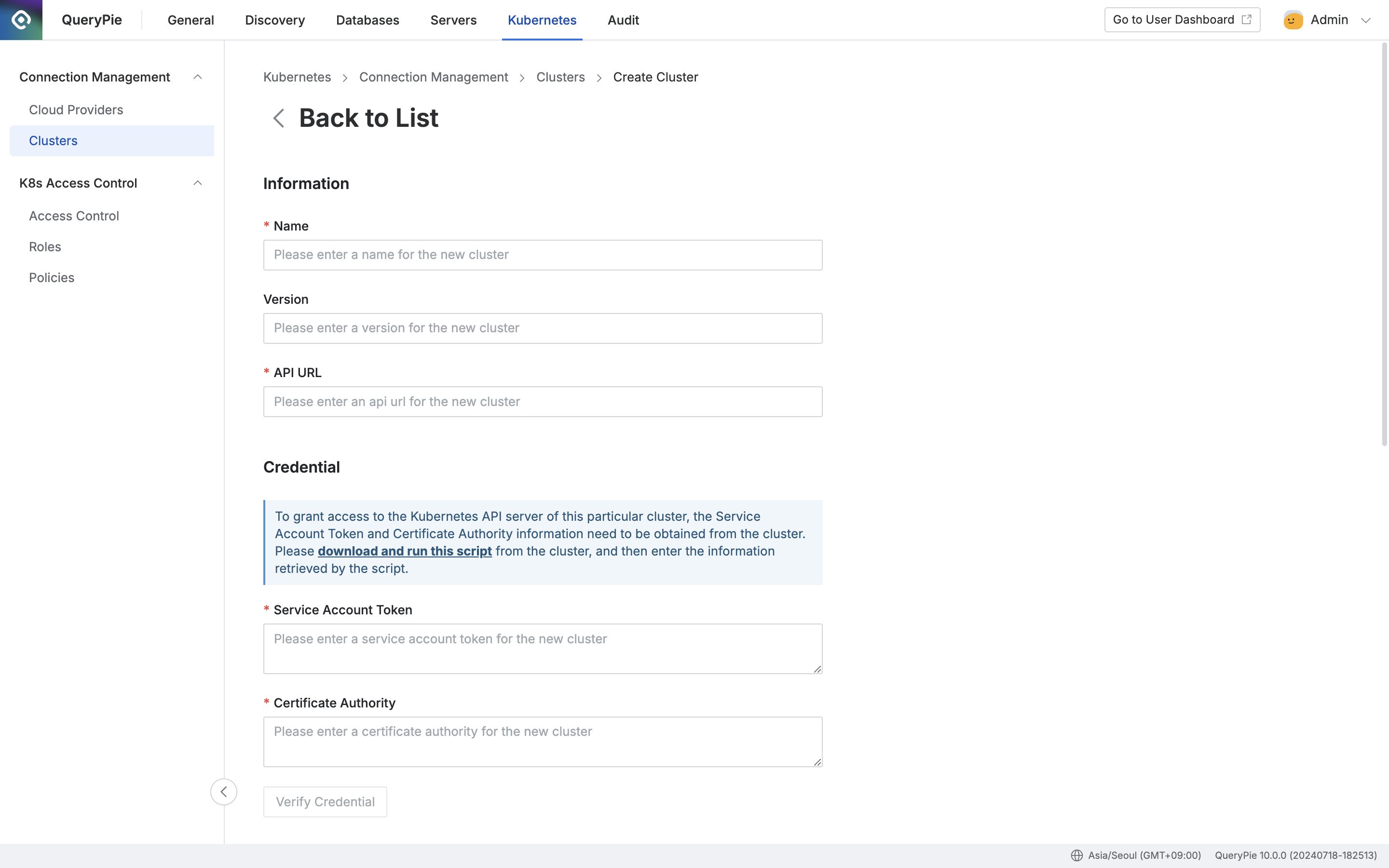
- Navigate to Administrator > Kubernetes > Connection Management > Clusters menu.
- Click the
+ Create Clusterbutton in the top right. - Information : Enter the following information for manual cluster registration
- Name : Enter a name that can identify the cluster. (Required)
- This information cannot be modified in the future.
- Version : Enter the cluster version. (Optional)
- This is an item that will be automatically filled through the credential authentication test procedure later.
- API URL : Enter the API URL of the cluster that will receive the Kubernetes API.
- Credential : To grant access to the Kubernetes API server of the cluster, you need to obtain the service account token and CA certificate from the cluster. Please check the content in the blue information box for details.
- Service Account Token : Enter the service account token value of the Kubernetes cluster that will be used when QueryPie Proxy makes user Kubernetes API calls.
- Certificate Authority : Enter the CA certificate that QueryPie will use to verify the Kubernetes API server certificate.
- Verify Credential : This button is activated when both the service account token and CA certificate are entered. Click the button to check if normal connection is possible. The result is displayed as follows based on the execution result:
- ✔️ Verified : Indicates that the cluster connection was successful and the service account token and CA certificate were entered correctly.
- ❌ Verification Failed : Indicates that the cluster connection failed, there may be an error in the service account token and CA certificate values, or network connection failed.
- Logging Options : Select logging options for the cluster.
- Request Audit : This is an option to enable logging for Kubernetes API call history for the cluster, and the default is
On. When this function is switched toOff,- Kubernetes API call history for the cluster will not be recorded.
- All Request Audit Types and Pod Session Recording below are bulk deactivated.
- Request Audit Types : Administrators can select the target Verb to audit for the cluster. The default selects all of the following basic verbs.
- Verb types:
getlistwatchcreateupdatepatchdeletedeletecollection
- ✅ Select All : Audits all API calls.
- Verb types:
- Pod Session Recording : This is an option to enable recording for sessions opened by Pod exec commands within the cluster, and the default is
On. This function is switched toOffif the following conditions are not met:- Request Audit must be enabled to
On. - The following verbs must be selected in Request Audit Types:
createget
- Request Audit must be enabled to
- Request Audit : This is an option to enable logging for Kubernetes API call history for the cluster, and the default is
- Name : Enter a name that can identify the cluster. (Required)
- Tags : You can manually enter tags for individual clusters if necessary, and for clusters synchronized through Cloud Providers, synchronized tags are also displayed. (However, tags imported through synchronization cannot be deleted or modified.) Click the
+ Add Tagbutton to add a new row and enter the desired tag value, and tags must be entered in key-value format.- Key : Enter a Key value that can distinguish the tag within 512 characters.
- Key value must be entered as required, and already registered keys cannot be entered in duplicate.
- Duplicates are checked case-sensitively.
- Value : Enter a Value value to be used for filtering within 256 characters.
- Key : Enter a Key value that can distinguish the tag within 512 characters.
- After going through the above process, click the final
Savebutton to successfully register the cluster.
Kubernetes Cluster Integration Script Usage Guide
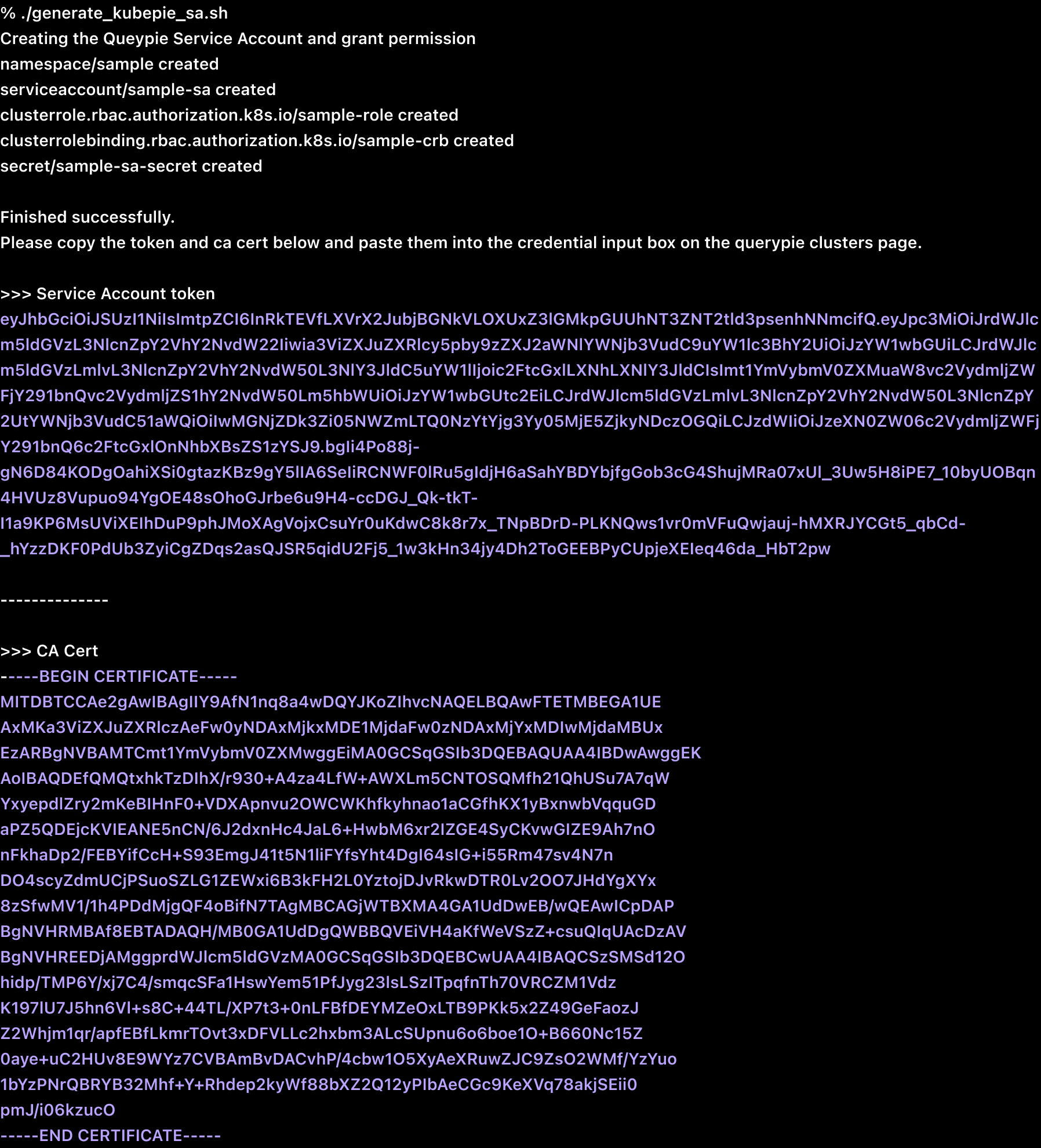
- Administrators must be able to access the target Kubernetes cluster in advance.
- Administrators can download the script by clicking the “download and run this script” link in the Credential information box at Administrator > Kubernetes > Connection Management > Clusters > Create Cluster > Credential.
generate_kubepie_sa.sh script content
#!/bin/bash
set -o nounset -o errexit -o pipefail
RESOURCE_PREFIX=querypie
NAMESPACE=querypie
SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME=${RESOURCE_PREFIX}-sa
CLUSTER_ROLE_NAME=${RESOURCE_PREFIX}-role
CLUSTER_ROLE_BINDING_NAME=${RESOURCE_PREFIX}-crb
SERVICE_ACCOUNT_SECRET_NAME=${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}-secret
echo "Creating the Queypie Service Account and grant permission"
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: ${NAMESPACE}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: ${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}
namespace: ${NAMESPACE}
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: ${CLUSTER_ROLE_NAME}
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- users
- groups
- serviceaccounts
verbs:
- impersonate
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: ${CLUSTER_ROLE_BINDING_NAME}
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: ${CLUSTER_ROLE_NAME}
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: ${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}
namespace: ${NAMESPACE}
EOF
SA_SECRET_NAME=$(kubectl get -n ${NAMESPACE} sa/${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME} -o "jsonpath={.secrets[0]..name}")
if [ -z $SA_SECRET_NAME ]
then
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
metadata:
name: ${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_SECRET_NAME}
namespace: ${NAMESPACE}
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: "${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}"
EOF
SA_SECRET_NAME=${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_SECRET_NAME}
fi
if [[ "$OSTYPE" == "linux-gnu" ]]; then
BASE64_DECODE_FLAG="-d"
elif [[ "$OSTYPE" == "darwin"* ]]; then
BASE64_DECODE_FLAG="-D"
elif [[ "$OSTYPE" == "linux-musl" ]]; then
BASE64_DECODE_FLAG="-d"
else
echo "Unknown OS ${OSTYPE}"
exit 1
fi
SA_TOKEN=$(kubectl get -n ${NAMESPACE} secrets/${SA_SECRET_NAME} -o "jsonpath={.data['token']}" | base64 ${BASE64_DECODE_FLAG})
CA_CERT=$(kubectl get -n ${NAMESPACE} secrets/${SA_SECRET_NAME} -o "jsonpath={.data['ca\.crt']}" | base64 ${BASE64_DECODE_FLAG})
echo "
Finished successfully.
Please copy the token and ca cert below and paste them into the credential input box on the querypie clusters page.
>>> Service Account token
${SA_TOKEN}
--------------
>>> CA Cert
${CA_CERT}"- After downloading the script, grant execution permissions and use it by executing the following command in the corresponding path.
chmod +x generate_kubepie_sa.sh ./generate_kubepie_sa.sh
Last updated on